Technological Innovation of Glufosinate Enterprises
Glufosinate still has room for growth, with a focus on seed promotion beyond GM oilseed rape and short-term mutational growth from paraquat bans in China, Thailand and Brazil. Glufosinate is the second largest non-selective herbicide in the world, and the market size has continued to grow in the past 10 years, reaching $920 million in 2018. The main growth points of future glufosinate demand are the accelerated promotion of glufosinate-tolerant GM soybeans and cotton crops in the U.S. and the replacement demand emerging from paraquat bans in China, Southeast Asia, and Brazil. The price reduction will help the promotion of glufosinate products.
Technical innovation of domestic glufosinate enterprises, low cost is the key to seize and expand the market. China, as the largest glufosinate production base in the world, is expected to add 10-30 thousand tons of production capacity in the future. The lowest cost method of glufosinate production is Bayer's continuous vapor phase method, which has very high process barriers. Although the process technology has not been replicated in China, a breakthrough has been made in some key steps (MDP). The cost performance of glufosinate relative to other non-selective herbicides will be more prominent. Low-cost leading companies will be more motivated to expand production against the backdrop of strong market demand due to the improved profitability brought by the process advancement, and thus their market share will continue to rise.
1. Glufosinate still has room for growth, with a focus on seed promotion beyond GM oilseed rape and short-term mutational growth from paraquat bans in China, Thailand and Brazil.
1.1 Glufosinate has become the second largest non-selective herbicide in the world
Glufosinate is a highly effective, broad-spectrum, low-toxicity non-selective herbicide developed by Hearst Corporation in the 1980s, second only to glyphosate and paraquat, and the second most important genetically modified herbicide after glyphosate. The mechanism is that by inhibiting the production of glutamine synthetase, it can lead to disruption of plant nitrogen metabolism, excessive accumulation of amines, disintegration of chloroplasts and inhibition of photosynthesis, which eventually leads to plant death.
As one of the representatives of the four major non-selective herbicides, glufosinate has maintained a high growth trend in recent years. Although it cannot compete with glyphosate in terms of volume, it has overtaken paraquat to become the second largest non-selective herbicide in the world in 2016 and reached $920 million in 2018.
Research on the demand for glufosinate has been a shortage of research in the market, mainly constrained by the low frequency of pesticide data updates, long lag time, opaque customs data, and untimely access to overseas production and crop promotion information.
Generally speaking, the demand for glufosinate can be divided into two parts: one is the stock demand, and the other is the new demand.
1.2. GM oilseed rape has certain cyclical characteristics, and the overall new increase in the future is limited.
The commercialization of glufosinate-tolerant oilseed rape started in 1996, the same year as the global commercialization of GM crops, and is the earliest batch of GM crops in the world to be promoted commercially.
1.3 The spread of glufosinate tolerant transgenic crops in the US exceeded expectations
Glufosinate-tolerant transgenic soybeans, cotton and other seeds may become a new growth point for glufosinate demand. Scientists use alternate weed control strategies to develop GM crops with multiple herbicide resistance, so glufosinate and glyphosate demand are highly correlated. The incremental demand for this product has been ignored by the general market research, and the previous market consensus research expects that the new increment of glufosinate mainly lies in the replacement of paraquat.
1.4. Banning paraquat in China, Thailand and Brazil will continue to boost domestic demand and export of glufosinate
Paraquat substitution is also one of the main reasons for the incremental contribution of glufosinate ammonium chloride over the years and beyond. Paraquat, as a non-selective herbicide with excellent properties, has a large market space globally. However, due to the irreversibility of its toxicity, it has been gradually restricted or banned in developed and developing countries in recent years. China is the world's largest consumer of paraquat, and the amount of paraquat used in 2016 reached 12,000 tons, down 30% from three years ago, mainly because China took the first substantial step in banning paraquat in 2014. The Ministry of Agriculture withdrew the registration and production license of paraquat aqueous and stopped production. Since then, the ban on the sale of paraquat aqueous has been in effect since July 2016, and there will be no more sales and use of paraquat products on the Chinese market from September 2020. The ban on paraquat left a huge market vacuum that will be supplemented by glyphosate, glufosinate, diquat and other varieties.

2. The road of technological innovation for domestic glufosinate enterprises, low cost is the key to seize and expand the market
2.1. There are many production processes of glufosinate, and the barriers of low-cost process are high
The production barriers of glufosinate are high, and most of the domestic production capacity is by the Gellan method, which has low atomic economy, more triple wastes, and is prone to explosion. The lowest cost method of glufosinate production is Bayer's continuous vapor phase method, which has very high process barriers, although the domestic production capacity has not been replicated.
Although the process technology has not yet been replicated in China, with the continuous attempts of domestic glufosinate enterprises, breakthroughs have been made in some key steps, and the production cost of domestic glufosinate is expected to be significantly reduced.
The synthesis of glufosinate is mainly divided into two stages: (1) synthesis of key phosphine intermediates A/B/C/D. (2) Synthesis of glufosinate. In order to control the cost of industrial production, the route selection needs to consider the source and price of raw materials, reaction conditions and yields, safety and environmental protection. From a comprehensive point of view, the Bayer process is the best, which can realize a clean process with complete continuity, automation, no solvent, no odor and almost no waste residue. And the domestic glufosinate production route has obvious differences in the choice of step (1), which also reflects the differentiation of technology level.
Figure 1:Illustration of mainstream synthesis method of glufosinate
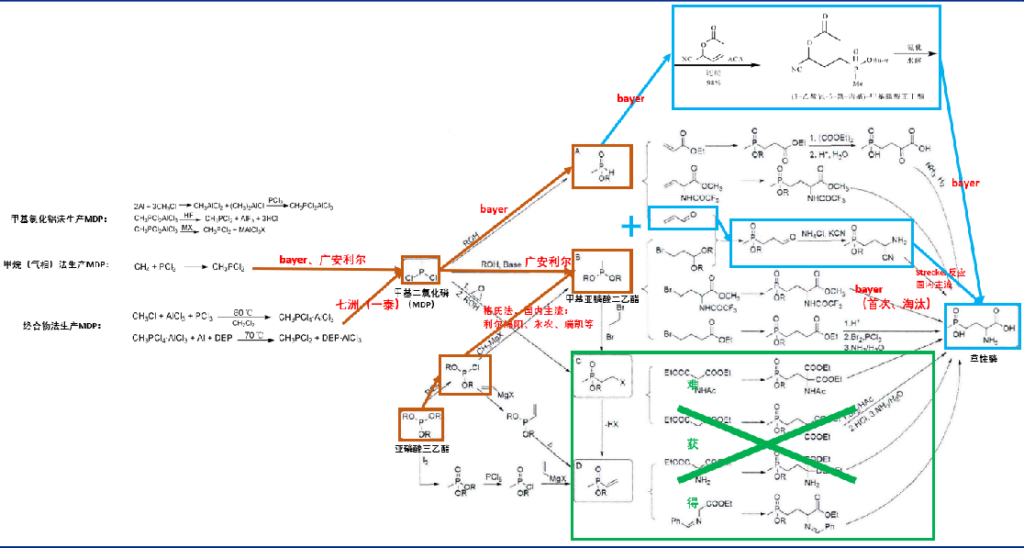
After the financial crisis, the boom of the agrochemical industry rose. Due to the expansion of the global ban on paraquat, the emergence of glyphosate-resistant superweeds and the promotion of glufosinate-resistant genetically modified rape, the demand for glufosinate expanded rapidly and the price also rose. Under the dual role of capacity expansion and process breakthrough, the price trend of glufosinate is downward. The low price highlights the cost performance and promotes the outbreak of new demand. The demand side of the industry may embark on a logic similar to that of consumer electronics. From the perspective of future glufosinate capacity expansion, the growth rate is higher than that of the industry demand, and the process cost is competitive. Glufosinate price may trend downward. Price reduction can continue to improve its cost performance. It is conducive to the promotion of the industry and to seize the market share of other non-selective herbicides. Glufosinate is expected to become the next 100,000-ton single product.

